For a long time, I had been traversing a long winding road for data extraction from SQL Server. Initially, I was using MS BI Studio to connect MS SQL Server to Excel to extract data from SQL Server and write it to .csv format. Which was then imported into R data frame. This process was indeed cumbersome to me. My recent involvement with R and its majestic features have indeed got me hooked to it. So, to cut the story short in this post we will see how to connect R to SQL Server 2014 and manipulate the SQL database tables in R data frames. So let’s get started.
Creating an ODBC DSN Data Source The first time you connect R to your SQL Server instance you need to perform a few one-time set up tasks as follows;
- Create an ODBC DSN data source
- Install the necessary R ODBC package from CRAN
a. Create DSN
First we need to setup a user DSN data source pointing at our SQL Server using ODBC. The data source will be called from R using the package “RODBC”
b. Open “Administrative Tools” and “ODBC Data Sources (32 bit)”
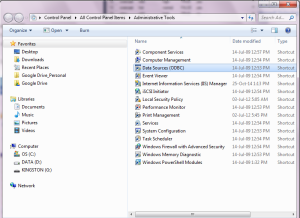
c. On the tab “User DSN” press “Add”
d. Select “SQL Server” in the provider list
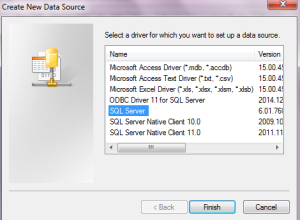
e. Now give the data source a name and a description. Remember this name – you will need it later on in the process. Last provide the name of the server where the SQL Server is installed. Press “Next”.
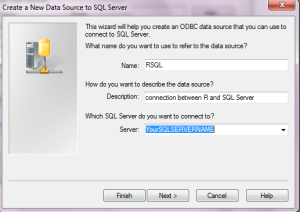
f. Select the way in which you will authenticate against the SQL Server. In this case we use the default settings as shown below and click “Next”.
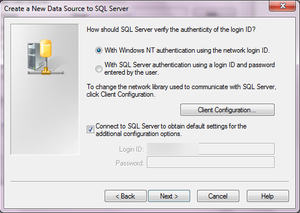
g. You now have the possibility to select the default database for the data source. What this means is that first put a check mark on “Change the default database to” and then click on the drop down arrow besides it and select your database name that you have created in SQL Server. Press “Next” and the “Finish”.
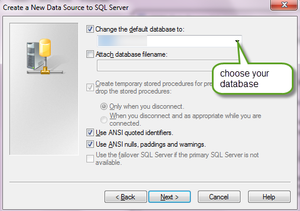
h. On the last page remember to press the “Test Data Source” button and ensure that the connection could be established.
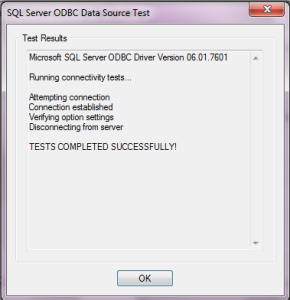
i. The User DSN is now created and active.
Install and load RODBC
Step 2:
- Support for SQL Server is not possible using native R – therefore we have to install the RODBC package from CRAN. Open up R and in the console window type:
install.packages(“RODBC”)
-
The RODBC packages is now downloaded and installed on your system. Next step is to load the package into R so the functions of the package can be used. In the console window type:
library(“RODBC”)
The RODBC package is now loaded and is ready
Connect SQL Server 2014 with R
Step 3: Now it is time to connect to the SQL Server database from R and retrieve a table
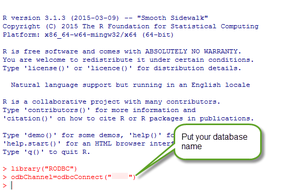
So for this example, I opened the connection like
> odbChannel=odbcConnect("YourDatabaseName")
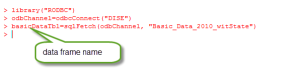
Now if you want to store your SQL Server database table to a data frame in R, it’s easy. Use the sqlFetch() command like given
> dataframeName=sqlFetch(odbChannel, “Your database table name”)
To get help on RODBC package use the RShowDoc command as follows
> RShowDoc (“RODBC”, package=”RODBC”) This will open up the pdf help version of RODBC package
To see what all tables as there in the database use sqlTables command as follows
> sqlTables (odbChannel, tableType=”TABLE”)
To execute a SQL query and store the result in a R data frame use the sqlQuery() function like
> dataFrameName=sqlQuery (odbChannel, “select * from tableName”)
I hope this tutorial helped you in connecting R with SQL Server 2014.
Cheers!
comments powered by Disqus